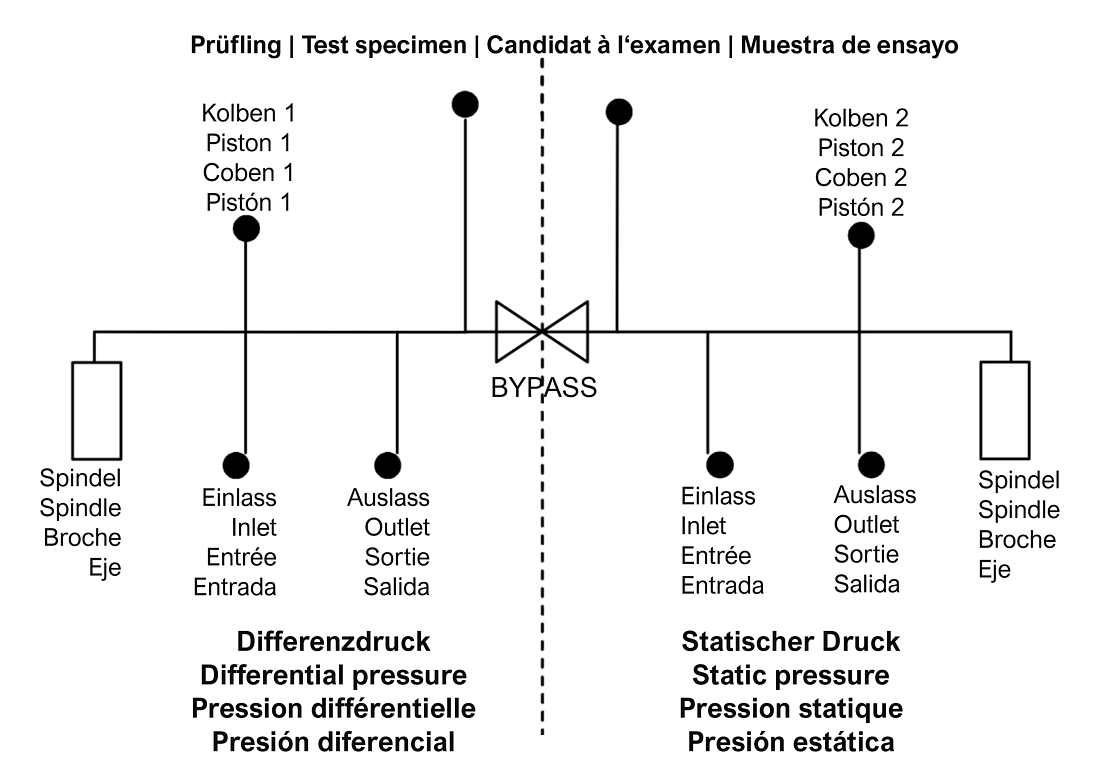
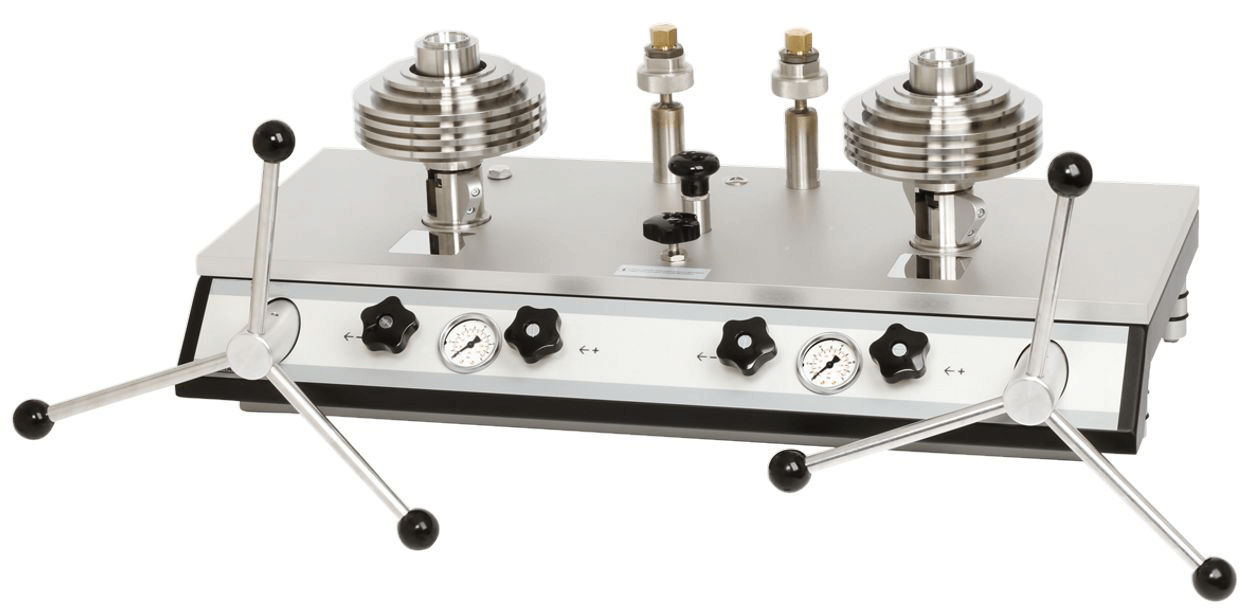
LR-Cal CPB5600-DP deadweight tester / pressure balance
Differential pressure at real static pressure


- Differential pressure with real static pressure
- Pressure ranges (= static pressure + differential pressure):
Pneumatic: 2 to 100 bar / 30 to 1,500 psi
(up to max. 400 bar pneumatic with integrated air to oil separator)
Hydraulic: 60 to 1.000 bar / 1,000 to 14,500 psi - Accuracy ±0.08% or ±0.015% of measured value
Description
LR-Cal CPB5600-DP description
Proven primary standard
Deadweight tester are the most accurate devices available on the market for the calibration of electronic or mechanical pressure measuring instruments. The direct measurement of the pressure (p = F/A), as well as the use of high quality materials allow a very small measurement uncertainty in combination with an excellent long-term stability of 5 years (recommendation according to the German Calibration Service (DAkkS). Pressure balances / deadweight tester have been used for years in factory and calibration laboratories of industry, national institutes and research institutes.
Autarkic operation
Due to the integrated pressure generation as well as the purely mechanical measuring principle, the LR-Cal CPB5600-DP differential pressure deadweight tester is also ideally suited for on-site use, maintenance and service.
Simple mode of operation
Depending on the unit design, the pressure is set either via an integrated pump or via an external pressure supply by means of metering valves. For fine adjustment, two very precisely adjustable spindle pumps with internally running precision spindles are installed.
As soon as the measuring system is in the hovering state, there is a balance of forces between pressure and mass supports. Due to the excellent workmanship of the system, this pressure remains stable for several minutes, so that pressure values for comparative measurement or more extensive adjustment work on the test specimen can be carried out without any problems.
As standard, the basic units are equipped with two connections for the piston-cylinder systems.
The test specimen is connected without tools to two quick-connection systems. A threaded insert with a G 1/2 female thread is included as standard. Further threaded inserts are optionally available, with which all common pressure gauges can be connected.
Special features:
- Measuring ranges (= static pressure + differential pressure)
up to 400 bar pneumatic
up to 1000 bar hydraulic - Total measurement uncertainty up to ±0.08% of reading plus 0.0001% (1 ppm) of static pressure
- With traceable factory calibration certificate as standard (option: DAkkS calibration certificate)
- Very high long-term stability, recommended recalibration only every 5 years
- Mass disks made of stainless steel, adaptation to local gravitational acceleration of the place of use possible without extra charge
Applications:
- Primary standard for calibration of differential pressure gauges under static pressure
- Reference instrument for factory and calibration laboratories for testing, adjusting and calibrating pressure measuring instruments of all types
- Self-sufficient complete system, also suitable for on-site use.
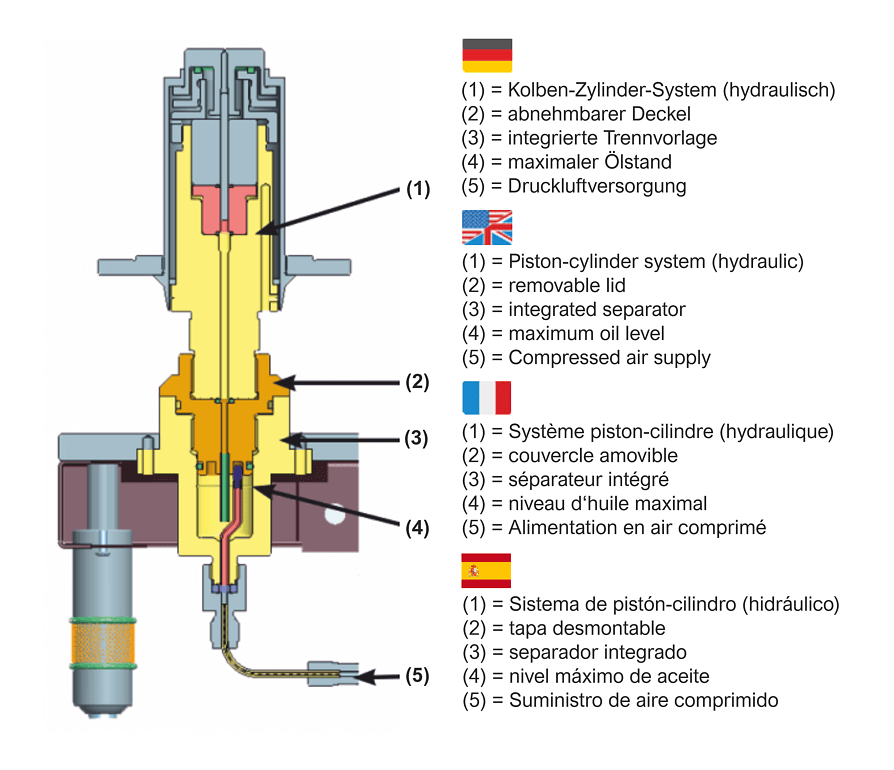
Piston cylinder system + mass set
LR-Cal CPB5600-DP piston cylinder system
The pistons and cylinders are made of tungsten carbide. Tungsten carbide has very low coefficients of pressure and temperature expansion compared to other materials, which results in very good linearity of the effective piston cross-sectional area and high accuracy.
Piston and cylinder are very well protected against contact, shock or contamination from the outside in a solid stainless steel housing. At the same time, an overpressure safety device is integrated, which prevents the piston from being pushed out vertically and thus prevents damage to the piston-cylinder system in the event of disc weights being removed under pressure.
The disc weights are stacked on a bell that is placed on the skirt of the piston. The design of the bell ensures a very low center of gravity for the weights placed on top, which minimizes the lateral forces on the piston-cylinder system and friction. For lower starting pressures, a lighter aluminum plate can be used in place of the bell.
The overall design of the piston-cylinder unit and the precise manufacture of the piston and cylinder ensure extremely low frictional forces, which result in excellent running characteristics with a high free rotation time and low sink rates. This ensures very high long-term stability. The recommended recalibration cycle is therefore five years depending on the conditions of use.
LR-Cal CPB5600-DP mass set
The standard set of measures (scope depending on measuring range) is supplied in storage case(s) with foam insert. This contains mass sets made of non-magnetic stainless steel, which are optimally matched to daily use. For differential pressure measurements, the use of class M1 or F1 fine incremental sets from the accessories is also recommended.
If you do not use the instrument under reference conditions (ambient temperature 20°C, air pressure 1,013 mbar, relative humidity 40%), appropriate correction calculations must be applied.
The pulley weights are manufactured as standard to the standard acceleration of gravity of 9.80665 m/s², but can also be adapted to their specific place (local gravity) of use.
The mass tables (list of number and weight of the pulley weights included in the mass sets can be found in the data sheet, see DOWNLOADs.
Pressure ranges + specification
LR-Cal CPB5600-DP pressure ranges + specification
| PNEUMATIC Range 1) 2) 6) |
bar | 0.03...2 | 0.2...10 | 0.4...50 | 0.4...100 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Required masses | kg | 10 | 10 | 10 | 20 | ||
| Smallest Step 3) | bar | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.25 | ||
| Sensitivity 4) | mbar | 0.002 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.05 | ||
| Nominal cross-sectional area of the piston | mm² | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | ||
| PNEUMATISC Range 1) 2) 6) |
psi | 0.435...30 | 2.9...150 | 5.8...500 | 5.8...1,000 | 5.8...1,500 | |
| Required masses | kg | 10 | 10 | 7 | 13 | 20 | |
| Smallest step 3) | psi | 0.2 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Sensitivity 4) | psi | 0.00003 | 0.00015 | 0.00075 | 0.00075 | 0.00075 | |
| Nominal cross-sectional area of the piston | cm² | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |
| HYDRAULIC Range 1) 2) 6) |
bar | 0.2...60 | 0.2...100 | 1...250 | 1...400 | 2...600 | 2...1,000 |
| Required masses | kg | 30 | 50 | 25 | 40 | 30 | 50 |
| Smallest step 3) | bar | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 |
| Sensitivity 4) | mbar | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Nominal cross-sectional area of the piston | cm² | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| HYDRAULIC Range 1) 2) 6) |
psi | 2.9...1,000 | 14.5...5,000 | 29...10,000 | 29...14,500 | ||
| Required masses | kg | 34 | 34 | 34 | 50 | ||
| Smallest step 3) | psi | 2 | 10 | 20 | 20 | ||
| Sensitivity 4) | psi | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.006 | ||
| Effective area | cm² | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.05 | ||
| Accuracy 7) | % of measured value |
proportion of static pressure: 0.0001 proportion of differential pressure: 0.015 / optional: 0.008 (high-pressure hydraulic version: 0.025 / optional: 0.020) |
|||||
| Lower limiting value of measurement uncertainty | depends on range; corresponds to sensitivity of piston | ||||||
| Basement versions | |||||||
| Pneumatic | up to 100 bar / 1,500 psi; with priming pump, spindle pump and port for external pressure supply | ||||||
| Pneumatic with separator | up to 400 bar / 5,000 psi; for external pressure supply, with integrared separator air on oil | ||||||
| Hydraulic | up to 1,000 bar / 14,500 psi; with internal pressure supply (on request version up to 1,600 bar / 23,200 psi available) |
||||||
| Pressure ports | |||||||
| Piston-cylinder-unit | Quick-fit connection for basement versions pneumatic and hydraulic; M30 x 2 male thread for basement version pneumatic with separator |
||||||
| Test item | 2 pcs. quick-fit connections 1/2" BSP female rotating, other threads see accessories | ||||||
| Pressure medium | |||||||
| Pneumatic | clean and dry non-corrosive gases (e.g. air or nitrogen) | ||||||
| Hydraulic | special oil (1 l included in supply) | ||||||
| Oil reservoir | cm² | 250 | |||||
| External pressure supply | 6 mm SWAGELOK (R) tube fitting; max. 110% of used pressure range (only for basement version pneumatic or version pneumatic with separator) | ||||||
| Materials | |||||||
| Piston | Tungsten Carbid | ||||||
| Cylinder | Tungsten Carbid | ||||||
| Set of masses | Stainless steel 1.4305 and aluminium, non-magnetic | ||||||
| Tubes / pipes in basement | |||||||
| Pneumatic | Stainless steel 1.4571, 3 x 1 mm | ||||||
| Hydraulic | Stainless steel 1.4404, 6 x 2 mm | ||||||
| Operating conditions | |||||||
| Operating temperature | °C | 18...28 | |||||
| Weight | |||||||
| Basement pneumatic | kg | 34.0 | |||||
| Basement pneumatic with separator | kg | 32.0 | |||||
| Basement hydraulic | kg | 38.5 | |||||
| Piston-cylinder-unit | kg | 1.5 (5.7 incl. bell jar and base weight, in optional carrying case (2 units required) | |||||
| BAR weight set, pneumatic | kg | 32.4 (incl. 2 wooden cases) | |||||
| BAR extension weight set, pneumatic | kg | 28.0 (incl. 2 wooden cases) | |||||
| BAR weight set, hydraulic | kg | 72.0 (incl. 2 wooden cases) | |||||
| BAR extension weight set, hydraulic | kg | 48.0 (incl. 2 wooden cases) | |||||
| PSI weight set, pneumatic | kg | 25.0 (incl. 2 wooden cases) | |||||
| PSI extension weight set 1, pneumatic | kg | 22.0 (incl. 2 wooden cases) | |||||
| PSI extension weight set 2, pneumatic | kg | 37,0 (incl. 2 wooden cases) only for range 1,500 psi | |||||
| PSI weight set, hydraulic | kg | 84,0 (incl. 2 wooden cases) | |||||
| PSI extension weight set, hydraulic | kg | 43,0 (incl. 2 wooden cases) | |||||
| Dimensions | |||||||
| Basement | mm | W 800 x D 375 x H 265 | |||||
| Wooden case for weight set | mm | W 400 x D 310 x H 310 | |||||
| Wooden case for extension weight set | mm | W 215 x D 310 x H 310 | |||||
| Optional case for piston-cylinder-unit | mm | W 300 x D 265 x H 205 | |||||
| Certificates | |||||||
| CE-Conformity | 97/23 EG (module A), only for versions above 1,000 bar | ||||||
| Calibration | Inspection certificate 3.1 according to DIN EN 10204 Optional DAkkS certificate, traceable and accredited according to ISO 17025 |
||||||
1) Measuring range = static pressure + differential pressure.
2) Theoretical starting value; corresponds to the pressure value generated by the piston (by its own weight). To optimise the operating characteristics, more weights should be loaded.
3) The smallest pressure change value that can be achieved based on the standard weight set. To reduce this, a set of trim-masses is available (see accessories).
4) The sensitivity is the threshold of the measuring system. It is the pressure value of the smallest mass-addition, which brings the piston-cylinder system clearly and reproducibly out of balance.
5) Measurement uncertainty assuming reference conditions (ambient temperature 20°C, air pressure 1,013 mbar, relative humidity 40%). Corrections must be calculated, if required.
6) Other on request.
7) The accuracy of the differential pressure is determined in accordance with the calculation basis shown in the datasheet (see DOWNLOADs).
Scope of standard supply
LR-Cal CPB5600-DP scope of standard supply
- Base unit LR-Cal CPB5600-DP with height adjustable feet
- Priming pump
- Connections for external pressure supply (only for pneumatic version)
- 2 spindle pumps for pressure generation and fine adjustment
- 2 connectors for piston cylinder systems
- 2 quick-fit connectors for item under test, with thread insert 1/2" BSP female, changeable
- 2 piston cylinder systems
- 2 sets of masses in carrying cases, calibrated to standard local gravity 9.80665 m/s²
- Special oil 1.0 liter (only for hydraulic version)
- Inspection certificate 3.1 according to DIN EN 10204
- Operating manual DE+EN
LR-Cal CPB5600-DP options + accessories
Accuracy ±0.008%of measured value

Option:
Increased accuracy
±0.008% from measured value
Calibration to speciallocal gravity
Option (without surcharge):
Mass sets manufactured to special local gravitational acceleration at the place of use of the device
(deviating from standard = 9.80665 m/s²)
DAkkScalibration certificate

Option:
DAkkS calibration certificate
traceable and accredited
according to ISO 17025
Incremental weight setclass F1

Accessory:
Fine incremental weight set class F1
1 mg to 50 g
A fine incremental weight set is strongly recommended for differential pressure deadweight tester.
Incremental weight setclass M1

Accessory:
Fine incremental weight set class M1
1 mg to 50 g
A fine incremental weight set is strongly recommended for differential pressure deadweight tester.
Case forpiston cylinder systems

Accessory:
Case for piston cylinder systems
Basic information on pressure balances see here...